Система
образования
Высшее образование в России — это перспективная инвестиция в свое будущее. Одним из главных преимуществ является получение качественных знаний и профессиональных навыков в определенной области, что позволяет выпускникам быть конкурентоспособными на рынке труда и достигать успехов в карьере.
Российское высшее образование обеспечивает возможность получения диплома или академической степени, которые признаются не только внутри страны, но и за ее пределами. Это открывает двери для различных карьерных возможностей и международного сотрудничества.
Уровни обучения
В России высшее образование имеет несколько уровней, каждый из которых представляет собой определенную ступень в образовательной лестнице студента. Но все они признаны за рубежом и полученный диплом дает выпускнику российского университета право на трудоустройство.
-

Бакалавриат в России — первая ступень в высшем образовании. Студенты изучают основную теоретическую базу и получают первый практический опыт в выбранном карьерном направлении.
После получения степени бакалавра студенты могут продолжить обучение по программе магистратуры, которая занимает два года и позволяет углубить свои знания и развить навыки.
Срок обучения составляет 4 года.
-
Программа специалитета сочетает в себе обучение по программе бакалавриата и магистратуры, предоставляя более глубокую специализацию в определенной области.
Срок обучения — 5-6 лет.
-
Магистратура — второй этап получения высшего образования, направленный на подготовку профессионалов с углубленными знаниями по специальности.
Получить степень магистра можно не только в том университете, где вы получили степень бакалавра. Выпускники могут рассмотреть для поступления другой университет. Обучение возможно на бюджетной или платной основе.
Срок обучения — 2 года.
-
Аспирантура — это уровень образования, предназначенный для подготовки научных кадров. Длительность обучения — от трех до четырех лет, в течение которых студенты занимаются научными исследованиями и пишут диссертацию.
-
Ординатура — это уровень образования, предназначенный для подготовки медицинских и фармацевтических работников. Длительность обучения, в зависимости от направления, составляет от двух до пяти лет.
-
Ассистентура-стажировка — это уровень образования, предназначенный для подготовки педагогических кадров по творческо-исполнительским специальностям. Длительность обучения — два года.
Преимущества высшего образования в России
Качество образования
Высшее образование в России известно своим высоким качеством обучения. Программы обучения в университетах разрабатываются с соблюдением всех стандартов высшего образования и учетом последних тенденций в различных областях науки.
Известность и признание дипломов
Дипломы, полученные в российских университетах, признаются и ценятся не только в стране, но и за ее пределами. Это открывает двери для студентов на международном рынке труда и предоставляет возможности для карьерного роста и развития не только в России, но и за рубежом.
Разнообразие специальностей
Высшее образование в России предлагает множество специальностей в различных областях. Будь то гуманитарные, естественные или технические науки, студенты имеют возможность выбрать ту область, которая соответствует их интересам и способностям.
Научные исследования
Российские университеты активно проводят научные исследования в различных областях. Студентам предоставляется возможность принять участие в исследовательских проектах, работать с ведущими учеными и применять полученные знания на практике. Это дает студентам ценный опыт и помогает развивать их научный потенциал.
Глобальное сообщество
Высшее образование в России привлекает студентов со всего мира, что создает многонациональное и межкультурное окружение. Это предоставляет студентам возможность общаться с представителями различных культур, расширять свои знания и развивать межкультурную коммуникацию.
Как развиваются университеты России
В России реализуются масштабные программы для комфортного и эффективного обучения студентов. Программа «Приоритет-2030» привлекает к сотрудничеству с университетами реальных представителей бизнеса, выделяет финансирование на исследовательские проекты и создает инновационную инфраструктуру в университетах. Комфортную среду для обучения и научных исследований создают в федеральном проекте «Создание сети современных кампусов» — уже сегодня построено 5 студгородков в разных регионах России. Передовые инженерные школы, созданные в университетах, готовят высококвалифицированных специалистов для ключевых отраслей экономики. В таких школах студенты участвуют в создании ключевых разработок в разных научных сферах.
Дополнительные сведения о программах, действующих в интересующих вас университетах, можно получить на их странице на портале Study in Russia.

Приоритет-2030
Программа «Приоритет-2030» позволяет сконцентрировать ресурсы для обеспечения вклада российских университетов в достижение национальных целей развития Российской Федерации, повысить научно-образовательный потенциал университетов и научных организаций, а также обеспечить участие университетов в социально-экономическом развитии субъектов Российской Федерации.
Цель программы «Приоритет-2030» – к 2030 году сформировать в России более 100 прогрессивных университетов — центров научно-технологического и социально-экономического развития страны.
В 2024 году в программе «Приоритет-2030» участвуют 142 университета из 56 регионов страны. Университеты ежегодно получают поддержку на реализацию своей программы развития. Сегодня благодаря программе в университетах создано:
- 38 новых лабораторий;
- 10 учебно-научных центров;
- более 60 новых образовательных программ;
- более 20 программ дополнительного профессионального образования;
- открыты 24 сетевые образовательные программы с ведущими отечественными и зарубежными университетами.
Узнать, входит ли университет в программу «Приоритет 2030», можно на странице этого университета на портале Study in Russia.
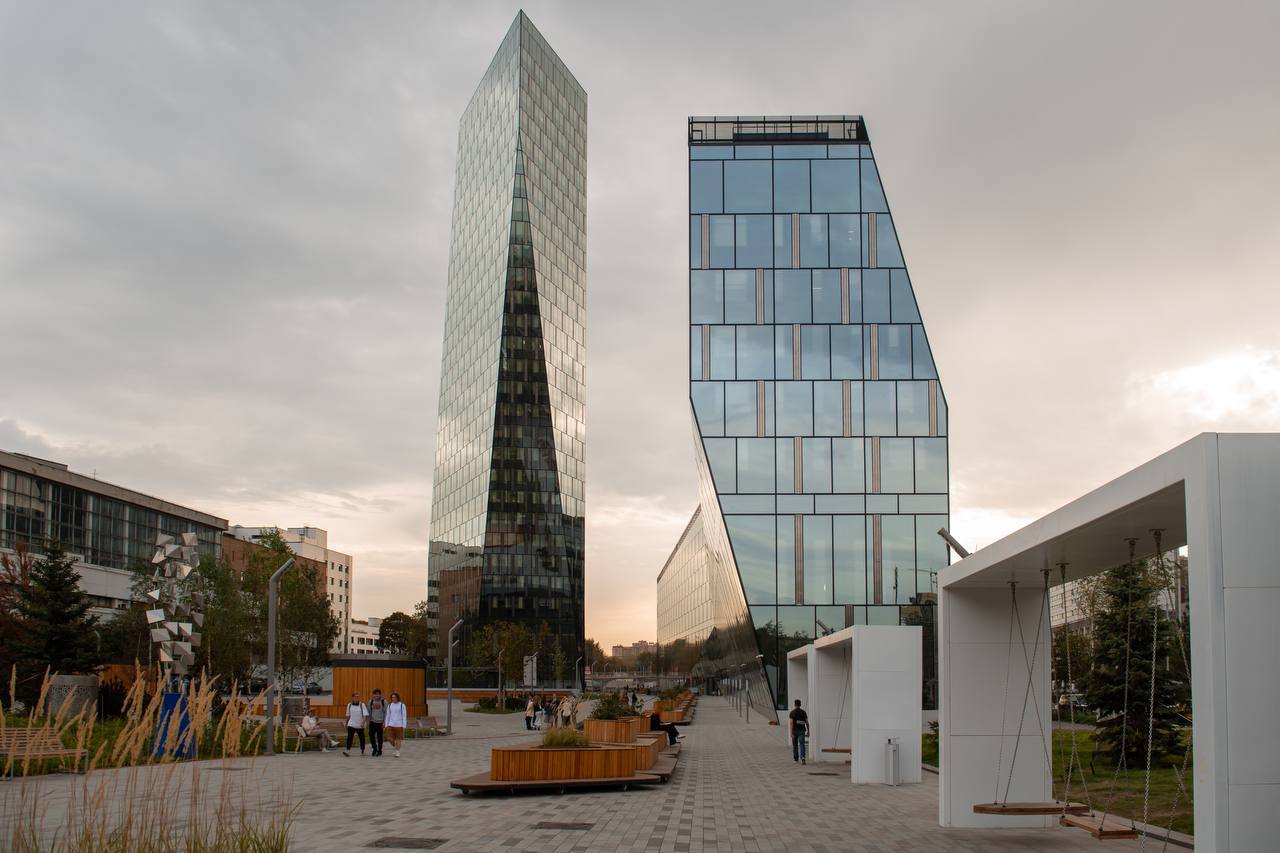

Создание сети современных кампусов
В России создается сеть из 25 университетских кампусов до 2030 года. Сейчас построено уже 18 зданий в 5 студгородках в Москве, Калининграде, Челябинске, Новосибирске, Нижнем Новгороде. Общая площадь — более 219 тыс. кв. м.
В кампусах предусмотрены все условия, чтобы студенты, аспиранты, преподаватели, молодые семьи могли учиться, работать и воспитывать детей.
Узнать, является ли университет участником федерального проекта «Создание сети современных кампусов», можно на странице этого университета на портале Study in Russia.
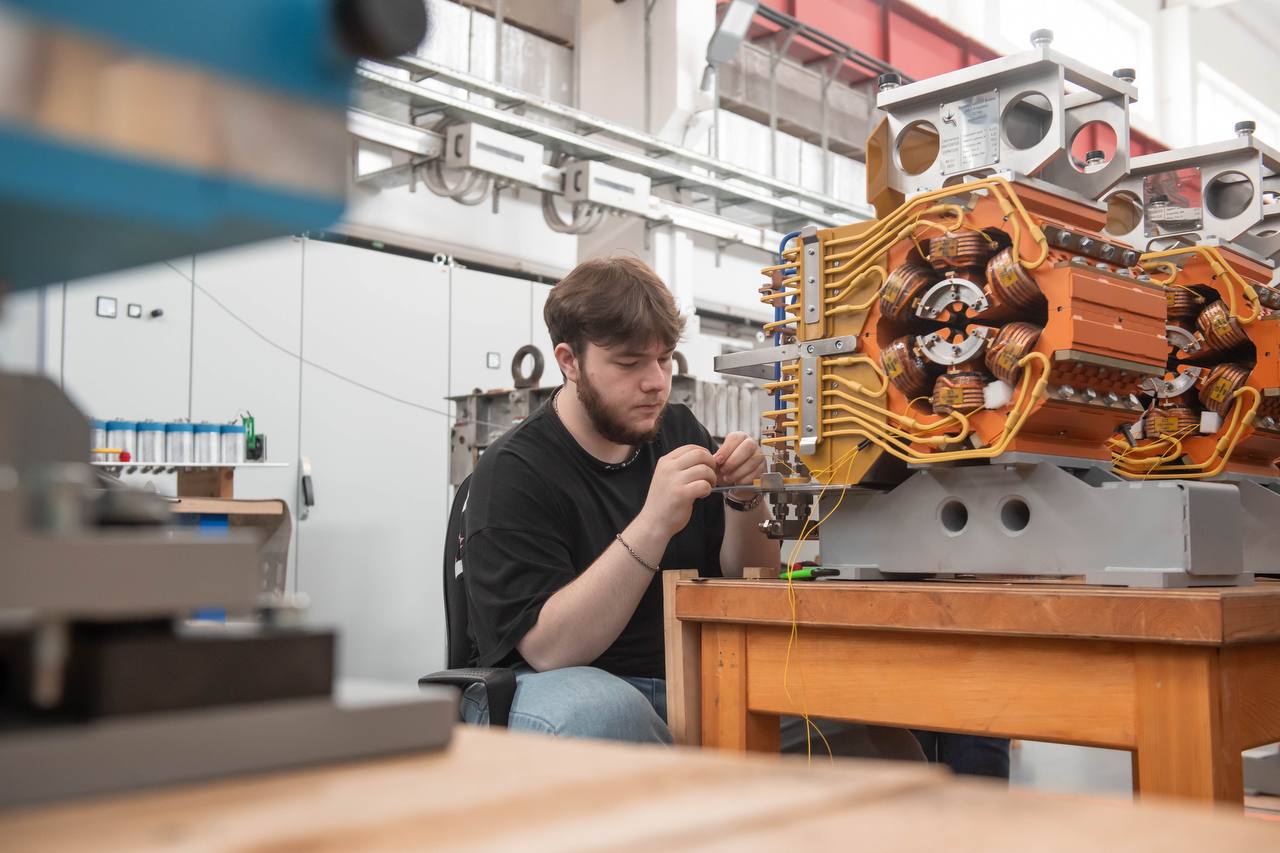

Передовые инженерные школы
На базе университетов России создано 50 передовых инженерных школ. Передовые инженерные школы дают студентам возможность получать практические навыки, участвовать в разработке инновационных решений и работать с ведущими индустриальными партнерами, готовясь к будущей карьере в стратегически важных сферах экономики.
Президент России В.В. Путин предложил расширить сеть передовых инженерных школ:
«Предлагаю расширить эту программу еще на 50 инженерных школ. То есть в общей сложности развернуть сеть по стране из 100 таких центров, которые будут готовить специалистов высшей квалификации и предлагать оригинальные технические решения, причем в самых разных областях, в промышленности, в сельском хозяйстве, в строительстве, транспорте, социальной сфере и, конечно, всегда и по каждому из этих направлений использовать искусственный интеллект».
Узнать, является ли университет участником федерального проекта «Передовые инженерные школы», можно на странице этого университета на портале Study in Russia.
Как учиться в России бесплатно?
Россия — одна из немногих стран мира, которая дает возможность иностранцам учиться бесплатно. Есть несколько вариантов, с помощью которых иностранец может поступить в университет России бесплатно. Некоторые категории иностранных граждан могут поступить в рамках общего конкурса наравне с гражданами России. Также каждый год Правительство Российской Федерации выделяет квоту для иностранных граждан на бесплатное обучение в российских университетах. Помимо этого, победители и призеры олимпиад, которые проводят университеты, могут быть зачислены без вступительных экзаменов или получить льготы при поступлении.
Дополнительные сведения о программах, действующих в интересующих вас университетах, можно получить на их странице на портале Study in Russia.
-
Некоторые категории иностранных граждан имеют право поступить в рамках общего конкурса на бюджетной основе. К таким категориям относятся:
1. Граждане Республики Беларусь, Республики Казахстан, Кыргызской Республики
Граждане этих республик при подаче документов на обучение, помимо основного пакета документов, прилагают копии нотариально заверенных переводов:
- документа, удостоверяющего личность: главная страница с фото и страница с пропиской при наличии;
- документа об образовании.
Также необходимо предоставить копию миграционной карты и копию талона-уведомления о постановке на миграционный учет.
2. Соотечественники, проживающие за рубежом
Абитуриенты данной категории при подаче документов на обучение, помимо основного пакета документов, прилагают копии нотариально заверенных переводов:
- документа, удостоверяющего личность: главная страница с фото и страница с пропиской при наличии;
- документа об образовании;
- документа, подтверждающего постоянное проживание за рубежом (например, копия страницы в паспорте, выписка из домовой книги);
- миграционной карты;
- талона-уведомления о постановке на миграционный учет;
- комплекта документов, подтверждающего либо наличие гражданства СССР у абитуриента, либо родство по прямой восходящей линии с лицами, имевшими гражданство СССР.
Например, один из родителей абитуриента являлся гражданином СССР. В таком случае необходимо предоставить копию документа, удостоверяющего личность родителя, в котором будет присутствовать отметка о месте рождения, и копию свидетельства о рождении абитуриента, в котором указан данный родитель.
-
Для получения дополнительной информации и подачи заявки на квоту:
- зарегистрируйтесь на портале Россотрудничества;
- дождитесь приглашения для участия в отборочных мероприятиях в стране проживания;
- найдите себя на сайте в списке кандидатов, рекомендованных к прохождению второго этапа отбора;
- дождитесь письма на вашей электронной почте об открытии доступа к личному кабинету на портале;
- отслеживайте статус заявки в личном кабинете на портале.
О квоте Правительства России: часть 3 ст. 78 Федерального закона от 29.12.2012 г. № 273-ФЗ, а также Постановление Правительства РФ от 18.12.2020 г. № 2150.
-
Грантовая поддержка иностранных студентов в настоящее время прорабатывается.
-
В российских университетах регулярно проводятся конкурсы, в результате которых победители и призеры финального этапа могут быть зачислены в университет без экзаменов и в дальнейшем учиться бесплатно или же получить различные льготы при поступлении. Дополнительные сведения можно получить на странице конкретного университета на портале Study in Russia.
Также вы можете изучить перечень олимпиад, представленный на сайте.
Международная олимпиада Open Doors — еще одна возможность поступить в российский университет на бюджетное место. Победители и призеры могут зачисляться без вступительных экзаменов или получать дополнительные баллы при поступлении. Участники могут попробовать свои силы в 14 междисциплинарных профилях и получить шанс на бесплатное обучение в бакалавриате, магистратуре или аспирантуре российских универитетов. Олимпиада проходит в дистанционном формате и доступна на русском и английском языках.
Особенности приема иностранных граждан на обучение в российские университеты указаны в разделе 13 Приказа Министерства науки и высшего образования Российской Федерации от 21 августа 2020 г. № 1076.
История и традиции российского высшего образования
История высшего образования в России насчитывает более нескольких веков и богата традициями. Первые образовательные учреждения, подобные современным университетам, появились еще в Средневековой Руси. Одним из наиболее известных примеров таких учреждений является Московская Славяно-Греко-Латинская Академия, основанная в 1687 году.
Начало развитию высшего образования в России положил Петр I, подписав в 1724 г. указ об открытии в Санкт-Петербурге Академии наук.

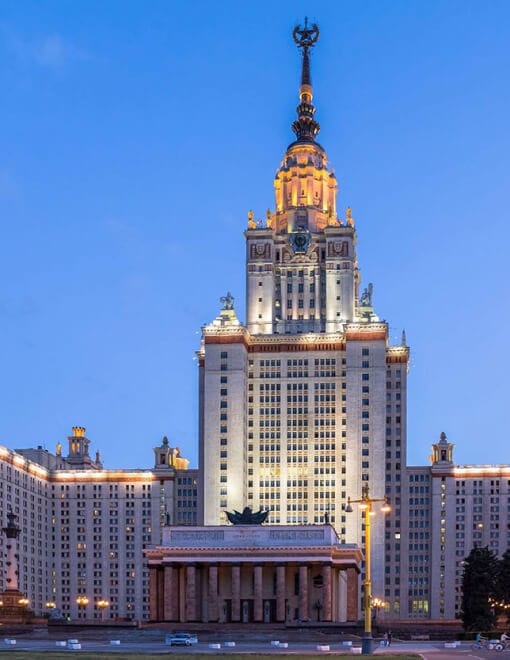
Стараниями Михаила Ломоносова, основоположника классического непрерывного образования в России, в 1755 году учрежден Московский государственный университет.
В XIX и XX веках высшее образование в России продолжило свое развитие и расширение. Были созданы новые специализированные университеты и институты, которые стали важными центрами научных исследований, образования и культуры. Российские ученые внесли значительный вклад в различные области науки и искусства, получив признание как в России, так и за ее пределами.

Традиции, развиваемые в российском высшем образовании, отличаются высокой степенью академической строгости и научной ответственности. Одним из ключевых аспектов российской системы образования является уклон на фундаментальное обучение, что означает углубленное изучение предметов и развитие широкого кругозора.
Российские студенты активно участвуют в научных исследованиях и проектах, конференциях и семинарах. Это позволяет им эффективно развивать свои профессиональные навыки, критическое мышление, навыки самостоятельной работы.
Сегодня Россия является одной из ведущих стран в области высшего образования. Многие российские университеты занимают высокие места в мировых рейтингах, а выпускники получают работу в крупных компаниях по всему миру.